Last Updated on 11/02/2026 by James Anderson
A Paradigm Shift in Psychiatry
For years, the primary use of Modafinil (Provigil) has been anchored in sleep medicine, with clear FDA approvals for narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and shift work sleep disorder (SWSD). However, a powerful narrative has been unfolding in psychiatry, driving its evolution from a niche wakefulness agent to a significant off-label tool in the mental health arsenal.
Psychiatrists, in their continuous search for effective treatments especially for stubborn symptoms like profound fatigue, cognitive “fog,” and treatment resistance have increasingly turned to Modafinil. This guide offers a comprehensive, clinically nuanced exploration of the question: “Do psychiatrists prescribe Modafinil?” We will dissect the scientific rationale, examine key psychiatric applications, navigate the critical decision-making process, and outline a framework for safe and ethical use.
Neuropharmacology: Understanding Why Psychiatrists Consider Modafinil
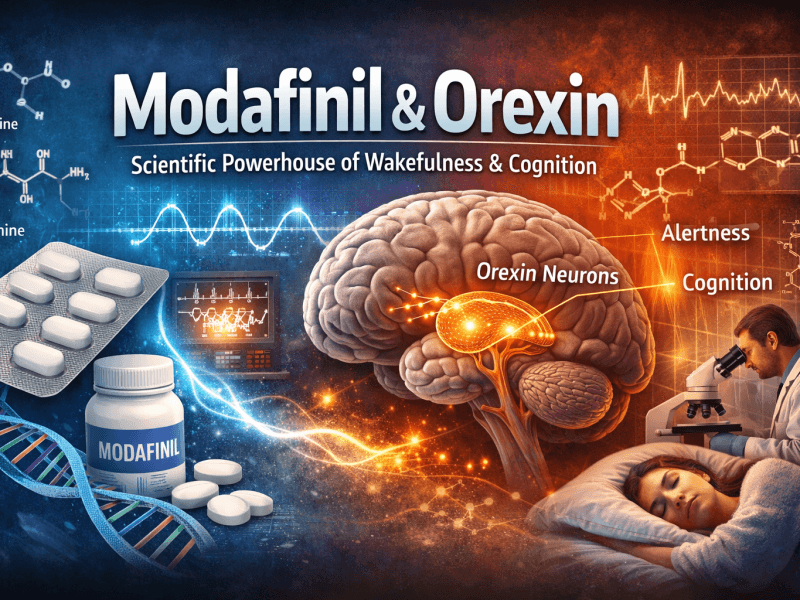
To comprehend its psychiatric appeal, one must move beyond the label of a “wakefulness drug.” Modafinil’s unique, multi-system neurochemical profile provides the mechanistic basis for its therapeutic effects on mood, motivation, and cognition.
Beyond Simple Stimulation: The Eugeroic Advantage
Modafinil is classified as a eugeroic (“good arousal”), distinct from classic stimulants (amphetamines, methylphenidate). While traditional stimulants cause a broad, often jittery CNS excitation via massive monoamine release, Modafinil promotes a state of sustained, clear-headed alertness. It achieves this through a more selective and nuanced modulation of key neurotransmitter systems:
| Neurotransmitter/System | Primary Mechanism | Clinical Relevance in Psychiatry |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | Inhibits the dopamine transporter (DAT), increasing extracellular dopamine, particularly in the striatum and nucleus accumbens. | Enhances motivation, reward processing, and executive function. Central to treating apathy and cognitive slowing. |
| Norepinephrine | Increases extracellular norepinephrine in the cortex and hypothalamus. | Improves attention, vigilance, and the “alerting” network of the brain. Crucial for focus and arousal. |
| Histamine | Activates tuberomammillary nucleus neurons, increasing histamine release. | A primary driver of cortical activation and wakefulness without significant anxiety induction. |
| Glutamate/GABA | Modulates the balance, potentially increasing excitatory (glutamate) and decreasing inhibitory (GABA) tone in specific circuits. | May enhance synaptic plasticity and cognitive processing speed, relevant for cognitive deficits. |
| Orexin (Hypocretin) | Likely stimulates orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus. | Stabilizes wakefulness and regulates energy homeostasis, linking arousal with motivated behavior. |
This targeted, multi-pathway action results in a favorable side effect and abuse-liability profile compared to Schedule II stimulants, making it an attractive option for psychiatrists managing complex, often chronic, conditions.
Primary Off-Label Psychiatric Applications: The Evidence
While not FDA-approved for psychiatric disorders, Modafinil’s use is supported by a growing body of research and is featured in some clinical practice guidelines as an adjunctive strategy.
1. Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD)
This is one of the most common and well-supported off-label uses.
- Target Symptom: Residual fatigue and excessive sleepiness, which are among the most persistent and disabling symptoms of depression, often lingering even after mood improves with first-line antidepressants like SSRIs.
- The Evidence: Numerous randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have shown that adjunctive Modafinil (typically 100-200 mg/day) can significantly reduce fatigue, improve wakefulness, and provide a modest boost to overall depressive symptoms and remission rates. It appears to work synergistically with conventional antidepressants.
- Psychiatric Rationale: It directly counteracts the hypoarousal and psychomotor retardation common in depression, allowing patients to engage more fully in therapy and daily activities.
2. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Target Symptom: Inattention, poor focus, and executive dysfunction in adults who cannot tolerate or do not respond adequately to first-line stimulants.
- The Evidence: Robust evidence supports its efficacy. A key meta-analysis in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry concluded it is an effective and generally well-tolerated treatment for adult ADHD. It is approved for ADHD in several European countries (as Sparlon®), though not in the U.S.
- Psychiatric Rationale: Its dopamine and norepinephrine effects improve attention and cognitive control. Its lower abuse potential makes it suitable for patients with a history of substance use or those concerned about stimulant misuse.
3. Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia
- Target Symptom: Cognitive negative symptoms, such as avolition (lack of motivation), anhedonia, and impaired executive function. These symptoms are largely untreated by antipsychotics and are major barriers to functional recovery.
- The Evidence: Research shows Modafinil can improve performance on cognitive tasks measuring working memory, attention, and cognitive flexibility. Effects on overall negative symptoms are more mixed but promising in some studies.
- Critical Caution: There is a small but documented risk of exacerbating psychosis or inducing agitation. Therefore, its use requires extreme caution, stable psychosis, and close monitoring by a specialist.
4. Bipolar Depression
- Target Symptom: Depressive episodes, particularly with prominent fatigue.
- The Evidence & Controversy: Studies show potential antidepressant effects. However, the primary concern is the risk of precipitating a manic or hypomanic switch. Most psychiatrists consider this a relative contraindication or reserve it for highly refractory cases under very close supervision, often with concurrent mood stabilizers.
- Psychiatric Rationale: If used, it aims to improve energy without the destabilizing risk profile of traditional antidepressants in bipolar disorder.
5. Medication-Induced Sedation
- Target Symptom: Debilitating fatigue caused by psychiatric medications themselves, such as certain antipsychotics (quetiapine) or mood stabilizers.
- Practice: Psychiatrists may use low-dose Modafinil (50-100 mg) to counteract sedation, allowing patients to continue an otherwise effective primary medication.
The Psychiatrist’s Decision-Making Framework: Who Is a Candidate?
A responsible psychiatrist does not prescribe Modafinil based on a patient’s request alone. The decision follows a rigorous, individualized risk-benefit analysis.
Key Evaluation Criteria:
- Confirmed Diagnosis & Symptom Profile: Is the primary condition (MDD, ADHD) well-established? Are the target symptoms (fatigue, inattention) prominent and functionally impairing?
- Treatment History: Is Modafinil being considered as a first-line treatment or an adjunct after failed trials of standard therapies (SSRIs, stimulants for ADHD)?
- Medical & Psychiatric Comorbidities:
- Absolute Contraindications: History of psychosis (for non-schizophrenia use), unstable cardiac disease, severe hepatic impairment.
- Relative Contraindications/Red Flags: History of mania/bipolar disorder, severe anxiety, active substance use disorder, uncontrolled hypertension.
- Risk of Interactions: The psychiatrist will meticulously review all medications. The most critical interaction is with hormonal contraceptives (pills, patches, rings), as Modafinil induces liver enzymes (CYP3A4) and can render them ineffective. A non-hormonal backup method is mandatory.
- Patient Goals & Informed Consent: The conversation must clearly establish realistic expectations (“for energy, not euphoria”), review potential side effects (headache, insomnia, anxiety, rare serious rash), and confirm the patient’s understanding of the off-label nature of the prescription.
Comparison: Modafinil vs. Traditional Psychiatric Agents
| Medication (Class) | Primary FDA Use | Mechanism Relevant to Psychiatry | Advantages in Psychiatry | Disadvantages/Risks in Psychiatry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modafinil (Eugeroic) | Narcolepsy, SWSD, OSA | DAT inhibition, NE/Histamine increase. | Clean alertness, low abuse potential (Schedule IV), few weight or metabolic issues. | Off-label use, can worsen anxiety/psychosis, critical contraceptive interaction. |
| Amphetamine (Stimulant) | ADHD, Narcolepsy | Potent DA/NE release and reuptake inhibition. | Potent, fast-acting for focus and energy. | High abuse/addiction potential (Schedule II), anxiety, insomnia, cardiovascular risk, mood crashes. |
| Methylphenidate (Stimulant) | ADHD, Narcolepsy | DA/NE reuptake inhibition. | Well-established for ADHD. | Similar abuse/addiction potential (Schedule II) as amphetamines, can cause anxiety. |
| Bupropion (NDRI Antidepressant) | MDD, Smoking Cessation | NE/DA reuptake inhibition. | Activating, helps with fatigue and ADHD symptoms, low sexual side effects. | Seizure risk at high doses, contraindicated in eating disorders, can increase anxiety. |
| SSRIs (Sertraline) | MDD, Anxiety | Serotonin reuptake inhibition. | First-line for depression/anxiety, non-addictive. | Often cause or worsen fatigue/sedation initially, sexual dysfunction, delayed onset. |
When a Psychiatrist Might Choose Modafinil: For residual SSRI fatigue, adult ADHD with stimulant intolerance, or cognitive deficits in stable schizophrenia where traditional stimulants are deemed too risky.
Navigating the Conversation with Your Psychiatrist: A Patient’s Guide
If you believe Modafinil could be helpful, here is how to approach a constructive discussion:
- Focus on Symptoms, Not the Drug: Start by describing your challenges in detail: “Despite my antidepressant, I still struggle with crippling fatigue that keeps me from work,” or “My ADHD medication helps but makes my anxiety unbearable.”
- Review Your History: Be prepared to discuss what medications you have tried, at what doses, for how long, and what side effects or benefits you experienced.
- Ask Informed Questions: Demonstrate you are a collaborative partner by asking:
- “Based on my diagnosis and history, do you think Modafinil could address my specific symptoms of fatigue/cognitive fog?”
- “What are the specific risks in my case, given my history of anxiety?”
- “How would we monitor for effectiveness and side effects?”
- “What is the plan if it doesn’t work or causes problems?”
- Respect the Professional Judgment: Understand that a psychiatrist’s decision to prescribe (or not) is based on complex clinical reasoning. If they decline, ask, “Can you help me understand why?” and “What alternative strategies can we try?”
Ethical & Practical Prescribing Considerations
- Off-Label ≠ Experimental: Off-label prescribing is legal, common, and often supported by peer-reviewed evidence. However, it requires thorough documentation of the rationale.
- Diversion and Misuse: While abuse potential is low, psychiatrists are vigilant about the risk of diversion for academic or cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals. Prescriptions are carefully managed.
- Monitoring: Initial follow-up is typically within 2-4 weeks to assess efficacy, side effects (especially mood changes or anxiety), and vital signs (blood pressure).
FAQ
Is it common for psychiatrists to prescribe Modafinil for depression?
It is a recognized and relatively common adjunctive strategy for treating residual fatigue and sleepiness in Major Depressive Disorder, particularly when first-line antidepressants have only partially worked. It is not typically a first-line or standalone antidepressant.
Can Modafinil help with anxiety?
Generally, no. It can often worsen anxiety. Modafinil’s activating properties can increase feelings of nervousness, agitation, and even induce panic attacks in predisposed individuals. It is usually contraindicated in primary anxiety disorders and used with great caution in patients with comorbid anxiety.
How is prescribing Modafinil different from prescribing Adderall?
The key differences are in schedule classification, abuse potential, and typical use. Adderall (Schedule II) has a high abuse potential and is a first-line treatment for ADHD. Modafinil (Schedule IV) has a low abuse potential and is more often used off-label for specific symptom clusters (fatigue, cognitive slowing) within other disorders or as a second-line ADHD treatment. The prescribing process for Schedule II drugs is also more stringent.
If my psychiatrist prescribes Modafinil, will my insurance cover it for an off-label use?
Coverage is highly variable and often denied for off-label indications. Your psychiatrist may need to submit a prior authorization with supporting clinical documentation. Be prepared to pay out-of-pocket or use a pharmacy discount card. Always check with your insurance provider first.
What should I do if I experience a side effect like a severe headache or a rash?
Common side effects like mild headache or nausea may subside. However, you must contact your psychiatrist immediately if you experience:
- Any new rash, blistering, or mouth sores (potential sign of serious reaction like Stevens-Johnson Syndrome).
- Chest pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath.
- Significant anxiety, panic, hostility, hallucinations, or suicidal thoughts.
Do not ignore these symptoms.
Conclusion
The answer to “Do psychiatrists prescribe Modafinil?” is a definitive yes, but with critical nuance. They prescribe it not as a panacea for low energy, but as a targeted, evidence-informed tool within a comprehensive treatment plan. Its value lies in addressing specific, debilitating symptom domains particularly fatigue and cognitive impairment that are often unresponsive to traditional psychotropics.
Successful use hinges on a careful patient selection process that meticulously weighs individual history, comorbid conditions, and potential risks. For the right patient, under the close supervision of a knowledgeable psychiatrist, Modafinil can be a powerful agent in reclaiming clarity, energy, and functional engagement in life. The journey begins with an open, informed, and collaborative dialogue with your mental health provider.
‼️ Disclaimer: The information provided in this article about modafinil is intended for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical consultation or recommendations. The author of the article are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or actions based on the information provided.
References:
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. PROVIGIL. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/020717s037s038lbl.pdf . 2015
- Ballon JS, Feifel D. A systematic review of modafinil: potential clinical uses and mechanisms of action. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006
- Willavize, S. A., Nichols, A. I., & Lee, J. Population pharmacokinetic modeling of armodafinil and its major metabolites. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.800 . 2016
- Fuxe K, et al. Modafinil enhances the increase of extracellular serotonin levels induced by the antidepressant drugs fluoxetine and imipramine: a dual probe microdialysis study in awake rat. Synapse. 2005
- Mechanisms of modafinil: A review of current research. nih.gov. 2007
- Woo, J., & Verduzco-Gutierrez, M. Traumatic brain injury: An overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and medical management. Medical Clinics of North America. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2019.11.001 . 2020
- Oliva Ramirez A, Keenan A, Kalau O, Worthington E, Cohen L, Singh S. Prevalence and burden of multiple sclerosis-related fatigue: a systematic literature review. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-021-02396-1 . 2021.
- Ciancio A, Moretti MC, Natale A, Rodolico A, Signorelli MS, Petralia A. Personality Traits and Fatigue in Multiple Sclerosis: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134518 . 2023
- Mereu, M., Bonci, A., Newman, A. H., & Tanda, G. The neurobiology of modafinil as an enhancer of cognitive performance and a potential treatment for substance use disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3232-4 . 2013
- Greenblatt, K., & Adams, N. Modafinil. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531476/ . 2023