Last Updated on 17/02/2025 by James Anderson
Understanding Narcolepsy and the Need for Effective Treatment
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy (sudden muscle weakness), sleep paralysis, and disrupted nighttime sleep. This condition significantly affects the quality of life, productivity, and overall well being of individuals. Managing narcolepsy requires a comprehensive approach, where effective pharmacological interventions play a pivotal role.
Symptoms of Narcolepsy
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness (EDS): The hallmark symptom, leading to unintentional naps and difficulty maintaining wakefulness.
- Cataplexy: Sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by strong emotions like laughter or surprise.
- Sleep Paralysis: Temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up.
- Hypnagogic Hallucinations: Vivid, often frightening sensory experiences during the transition between wakefulness and sleep.
The impact of these symptoms underscores the need for effective treatments like modafinil to restore wakefulness and improve the lives of narcolepsy patients.
Treatment of Narcolepsy with Modafinil
Modafinil is a wakefulness promoting agent widely regarded as a first-line treatment for excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy. Approved by the FDA, it has been demonstrated to improve alertness and reduce the frequency of unintentional naps.
Mechanism of Action
Modafinil primarily targets the brain’s sleep wake regulation centers, enhancing dopamine signaling. It increases the availability of neurotransmitters such as histamine and norepinephrine, which are critical for maintaining alertness. Unlike traditional stimulants, modafinil is not associated with significant euphoria or risk of dependence, making it a safer long term option.
Dosing and Administration
Modafinil is typically prescribed at doses of 200 mg once daily in the morning. In some cases, doses can be adjusted to a maximum of 400 mg daily based on individual response and tolerability. Patients are advised to follow their physician’s instructions to achieve optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing potential side effects.
Clinical Efficacy of Modafinil
Numerous clinical studies support the efficacy of modafinil in managing narcolepsy symptoms. Research consistently shows significant improvements in wakefulness and a reduction in excessive daytime sleepiness.
Key Findings from Clinical Trials
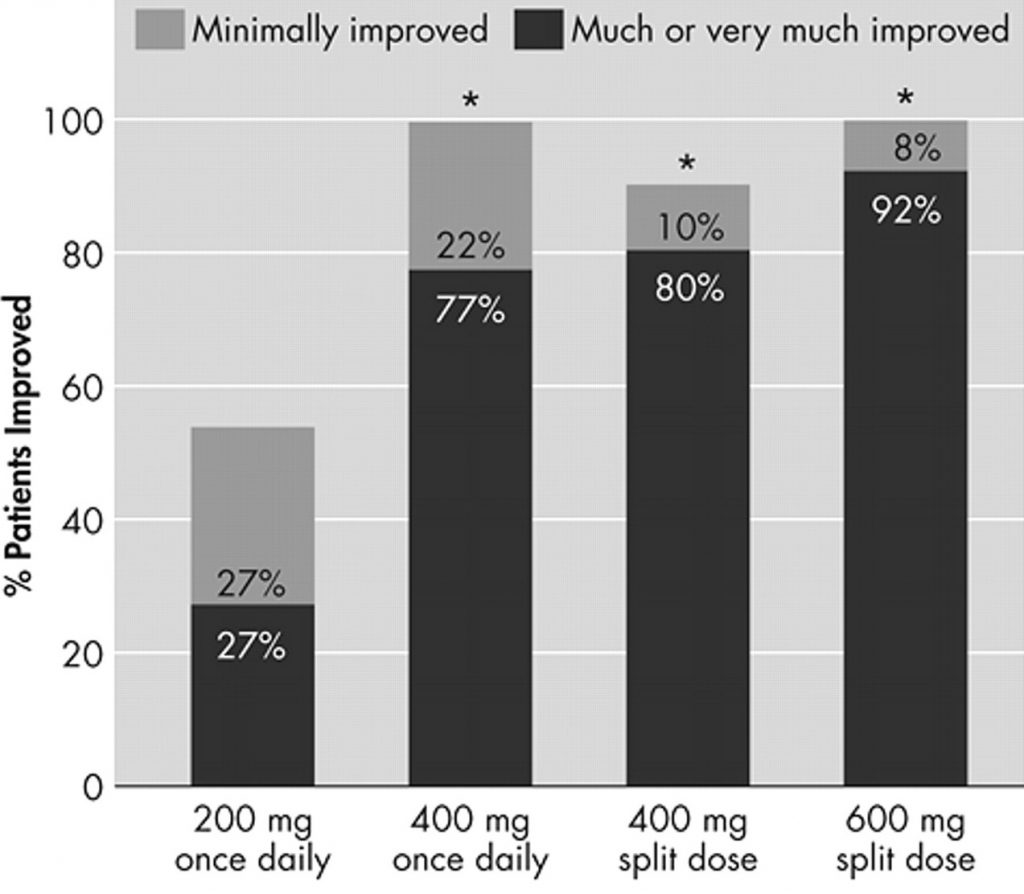
- Improved Wakefulness: A 12-week randomized controlled trial demonstrated that patients on modafinil reported higher scores on the Maintenance of Wakefulness Test (MWT) compared to a placebo group.
- Reduction in Sleep Episodes: Modafinil reduced the number of unintentional sleep episodes, enabling patients to engage in daily activities with fewer interruptions.
- Quality of Life Enhancement: Studies highlight improvements in cognitive performance, mood stabilization, and overall productivity among patients using modafinil.
These findings establish modafinil as an essential tool in the management of narcolepsy, offering measurable benefits that improve both clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Safety and Tolerability of Modafinil
Modafinil is generally well tolerated, with a favorable safety profile. However, like any medication, it may cause side effects in some individuals.
Common Side Effects
- Headache
- Nausea
- Nervousness
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
Rare but Serious Side Effects
- Severe Skin Reactions: Including Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- Psychiatric Symptoms: Such as anxiety, agitation, or hallucinations in predisposed individuals.
It is crucial for patients to communicate any adverse effects to their healthcare providers promptly. Modafinil is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or its components.
Modafinil vs. Other Treatments for Narcolepsy
While modafinil remains a cornerstone treatment for narcolepsy, other pharmacological options are available. Here, we compare modafinil with alternative therapies to illustrate its advantages and limitations.
Comparison with Traditional Stimulants
- Amphetamines and Methylphenidate: These traditional stimulants are effective but come with a higher risk of dependence, cardiovascular side effects, and insomnia compared to modafinil.
- Modafinil: Offers wakefulness-promoting effects without significant euphoria or abuse potential, making it a safer choice for long term use.
Comparison with Sodium Oxybate
- Sodium Oxybate: Particularly effective for managing cataplexy and disrupted nighttime sleep, but requires strict adherence to dosing schedules and is often less accessible due to cost.
- Modafinil: More widely available, easier to administer, and primarily addresses excessive daytime sleepiness.
Emerging Therapies
New treatments such as solriamfetol and pitolisant are showing promise in managing narcolepsy. However, their long term efficacy and safety profiles remain under investigation, whereas modafinil has a well established track record.
Conclusion
Modafinil represents a cornerstone in the pharmacological management of narcolepsy, offering significant improvements in wakefulness, cognitive performance, and overall quality of life. Its safety, tolerability, and efficacy make it a preferred choice for many patients and healthcare providers. While alternative therapies are available, modafinil’s unique benefits ensure its continued prominence in narcolepsy treatment protocols.
By understanding its clinical benefits and appropriate use, patients and providers can maximize outcomes, reducing the burden of narcolepsy on daily life.
‼️ Disclaimer: The information provided in this article about modafinil is intended for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical consultation or recommendations. The author of the article are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or actions based on the information provided.
References:
- Avidan, A. Y., and Kushida, C. A. The sodium in sodium oxybate: is there cause for concern? Sleep. Med. 2020
- Bassetti, C. L. A., Adamantidis, A., Burdakov, D., Han, F., Gay, S., Kallweit, U. Narcolepsy clinical spectrum, aetiopathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. 2019
- Bassetti, C. L. A., Kallweit, U., Vignatelli, L., Plazzi, G., Lecendreux, M., Baldin, E. European guideline and expert statements on the management of narcolepsy in adults and children. J. Sleep. 2021
- Cesta, C. E., Engeland, A., Karlsson, P., Kieler, H., Reutfors, J., and Furu, K. Incidence of malformations after early pregnancy exposure to modafinil in Sweden and Norway. 2020
- Dauvilliers, Y., Lecendreux, M., Lammers, G. J., Franco, P., Poluektov, M., Causse, C. Safety and efficacy of pitolisant in children aged 6 years or older with narcolepsy with or without cataplexy: a double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2023
- FDA approved drugs. 2024
- Hoy, S. M. Solriamfetol: a review in excessive daytime sleepiness associated with narcolepsy and obstructive sleep apnoea. CNS Drugs. 2023