Modafinil is a well known wakefulness promoting agent prescribed for conditions such as narcolepsy, sleep apnea, and shift work sleep disorder. While it has gained popularity among students, professionals, and individuals seeking cognitive enhancement, concerns about its safety remain, particularly for those with high blood pressure (hypertension).
How Modafinil Affects Blood Pressure
Modafinil functions by increasing dopamine levels in the brain while also influencing histamine, norepinephrine, and orexin systems. These changes contribute to enhanced alertness, focus, and cognitive performance. However, norepinephrine, a key stress hormone, plays a significant role in regulating blood pressure and heart rate.
For individuals with hypertension, Modafinil may increase systolic and diastolic blood pressure, especially when used in high doses. Several studies indicate that the drug can lead to a moderate but significant elevation in blood pressure and heart rate, making its use concerning for hypertensive patients.
Modafinil and Cardiovascular Risks
1. Increased Heart Rate (Tachycardia):
- Modafinil stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, which can lead to an elevated heart rate.
- For individuals already managing hypertension, this added strain can be risky.
2. Blood Pressure Spikes:
- Modafinil may cause a temporary rise in blood pressure, particularly if taken in high doses or in combination with other stimulants such as caffeine or nicotine.
- Those with uncontrolled hypertension should be cautious, as sudden spikes can lead to hypertensive crises.
3. Risk of Stroke and Heart Disease:
- Long term high blood pressure is a known risk factor for stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular complications.
- If Modafinil leads to a consistent elevation in blood pressure, it could worsen pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
Clinical Studies on Modafinil and Hypertension
Research examining the cardiovascular effects of Modafinil has produced mixed results. Some studies report no significant impact on blood pressure in healthy individuals, while others highlight mild to moderate increases in hypertensive patients. A 2018 study in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology found that Modafinil increases systolic blood pressure by approximately 3 – 5 mmHg on average, which can be concerning for those already at risk.
Who Should Avoid Modafinil?
While many individuals tolerate Modafinil well, certain groups should exercise caution:
- People with Severe Hypertension: Those with uncontrolled high blood pressure should avoid Modafinil unless approved by a physician.
- Individuals with Pre existing Heart Conditions: If you have a history of heart disease, arrhythmia, or stroke, Modafinil could increase cardiovascular risks.
- Elderly Individuals: Older adults are more susceptible to blood pressure fluctuations and should monitor their response to the drug carefully.
- Those Taking Other Stimulants: Combining Modafinil with caffeine, nicotine, or other stimulants can amplify its hypertensive effects.
Safe Usage Guidelines for People with High Blood Pressure
If you have hypertension but still wish to use Modafinil, follow these precautionary measures:
1. Consult a Doctor First
Before starting Modafinil, consult your healthcare provider. They may adjust the dosage or suggest alternative medications that have fewer cardiovascular effects.
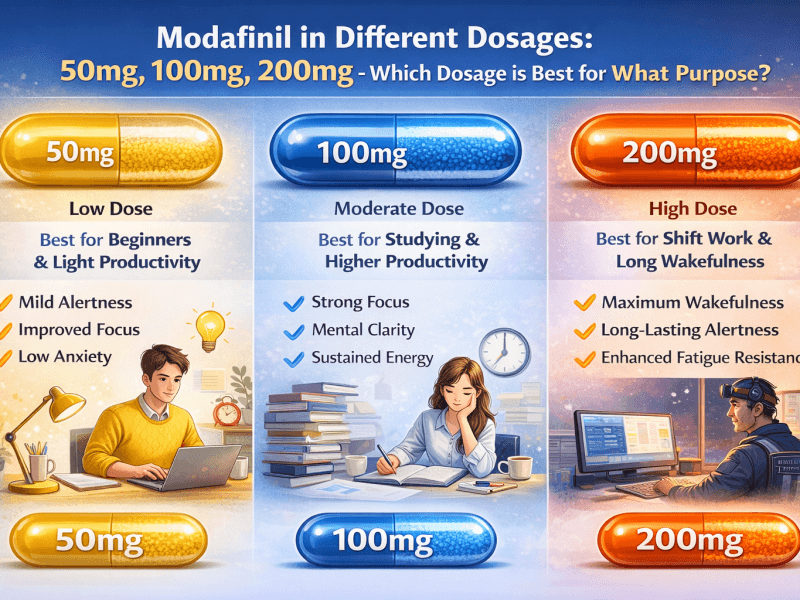
2. Start with the Lowest Effective Dose
A standard Modafinil dose is 200 mg per day, but individuals with hypertension may benefit from starting with 50 – 100 mg and monitoring their blood pressure response.
3. Monitor Your Blood Pressure Regularly
If you decide to take Modafinil, invest in a home blood pressure monitor and check your readings frequently. Any sustained increase should prompt a discussion with your doctor.
4. Avoid Other Stimulants
Modafinil already acts as a stimulant, so combining it with other substances like caffeine, nicotine, or pre-workout supplements could exacerbate hypertension risks.
5. Stay Hydrated and Maintain a Healthy Diet
Dehydration and poor diet choices (excess sodium, processed foods) can elevate blood pressure. Make sure to drink enough water and eat heart healthy foods.
6. Exercise Caution When Using Other Medications
Modafinil may interact with beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and other hypertension medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness.
Natural Alternatives to Modafinil for Cognitive Enhancement
If you have hypertension and want to enhance cognitive function without the risks associated with Modafinil, consider these natural alternatives:
- L-Theanine + Caffeine: A combination that improves focus without significant blood pressure elevation.
- Rhodiola Rosea: An adaptogenic herb that reduces fatigue and improves mental clarity.
- Ginkgo Biloba: Enhances blood circulation to the brain, supporting cognitive performance.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, known to support brain health and reduce inflammation.
- Bacopa Monnieri: A nootropic herb with memory enhancing properties.
Conclusion
Modafinil is a powerful cognitive enhancer, but it carries potential risks for individuals with hypertension. While some may tolerate it without issues, others may experience elevated blood pressure and heart rate, leading to cardiovascular concerns. If you have high blood pressure and are considering Modafinil, it is essential to consult a doctor, monitor your vitals, and take necessary precautions.
For safer cognitive enhancement, individuals with hypertension should explore natural alternatives that provide mental clarity and focus without the cardiovascular risks.
‼️ Disclaimer: The information provided in this article about modafinil is intended for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical consultation or recommendations. The author of the article are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or actions based on the information provided.
References:
- Hersey M, Tanda G. Modafinil, an atypical CNS stimulant? Pharmacological Advances in Central Nervous System Stimulants. Adv Pharmacol. 2024
- Robertson P, Hellriegel ET. Clinical pharmacokinetic profile of modafinil. Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 2003
- Kim D. Practical use and risk of modafinil, a novel waking drug. Environmental Health and Toxicology. 2012
- Modafinil. MedlinePlus. US National Library of Medicine. 2024
- Robert Auger R, Rowley JA, Hashmi SD. Treatment of central disorders of hypersomnolence: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine. 2021
- Kaplan S, Braverman DL, Frishman I, Bartov N. Pregnancy and Fetal Outcomes Following Exposure to Modafinil and Armodafinil During Pregnancy. JAMA Internal Medicine. 2021
- Slotnik DE. Michel Jouvet, Who Unlocked REM Sleep’s Secrets, Dies. 2017
- Greenblatt K, Adams N. Modafinil. StatPearls. Treasure Island, StatPearls Publishing. 2019
- Hashemian SM, Farhadi T. A review on modafinil: the characteristics, function, and use in critical care. Journal of Drug Assessment. 2020