Introduction to Modafinil
If wakefulness had a molecular signature, modafinil would be one of its most fascinating blueprints. Unlike classic stimulants that hit the brain like a hammer, modafinil works more like a skilled conductor subtle, precise, and remarkably efficient.
What Is Modafinil?
Modafinil is a wakefulness-promoting agent originally developed for the treatment of narcolepsy. Chemically distinct from amphetamines, it occupies a unique pharmacological niche. Clinically, it is known for enhancing alertness, sustaining attention, and reducing fatigue without producing the pronounced euphoria or crash associated with traditional stimulants.
Clinical Indications and Approved Uses
From a regulatory standpoint, modafinil is approved for narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea related residual sleepiness, and shift work sleep disorder. However, its neurochemical profile has attracted scientific interest far beyond these indications.
Understanding Norepinephrine
To understand modafinil, one must understand norepinephrine. The two are intimately linked in shaping alertness and cognitive control.
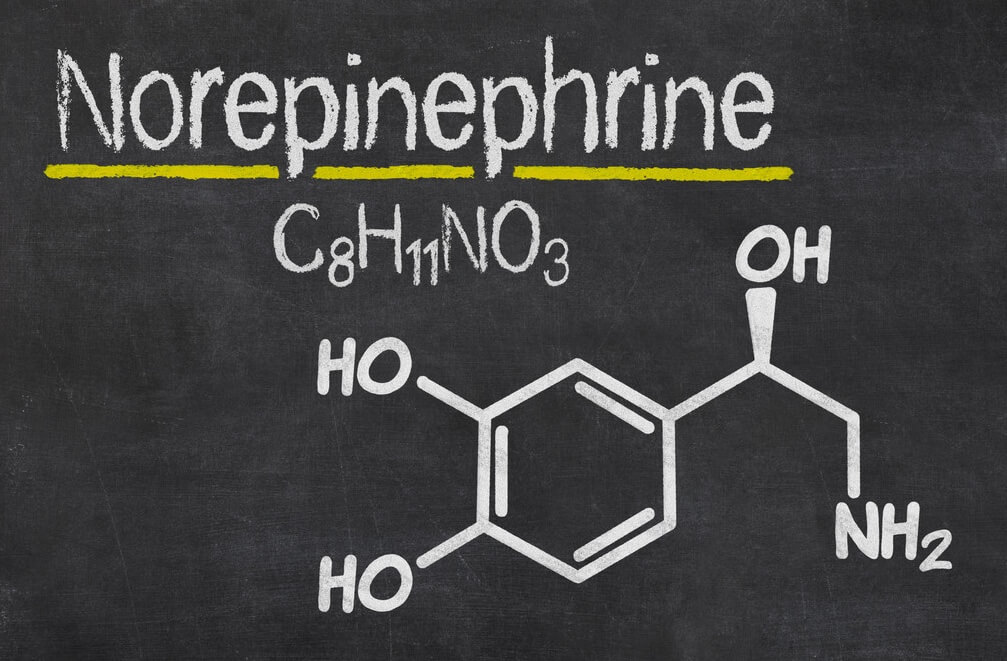
What Is Norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline, is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone. In the brain, it functions as a key regulator of arousal, vigilance, and stress responsiveness.
Norepinephrine as a Neurotransmitter and Hormone
In the central nervous system, norepinephrine modulates signal-to-noise ratio essentially helping the brain decide what matters and what does not. In the periphery, it participates in the classic “fight or flight” response.
Role in the Central Nervous System
Centrally, norepinephrine originates primarily from the locus coeruleus, a small but powerful nucleus in the brainstem. Despite its size, it projects widely across the cortex, hippocampus, and limbic system.
Role in the Peripheral Nervous System
Peripherally, norepinephrine increases heart rate, constricts blood vessels, and mobilizes energy stores. These effects become clinically relevant when drugs influence norepinephrine signaling.
The Neurobiology of Wakefulness and Attention
Wakefulness is not a switch it is a network.
Key Brain Regions Involved
The prefrontal cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus, and brainstem form an interconnected system that maintains alertness. Norepinephrine acts as a global modulator across this system.
Neurotransmitter Networks Regulating Arousal
Dopamine, histamine, orexin, acetylcholine, and norepinephrine work in concert. Modafinil touches several of these systems, but norepinephrine is one of its most consequential downstream effects.
How Modafinil Works in the Brain
Ask ten neuroscientists how modafinil works, and you may get ten nuanced answers. But patterns do emerge.
Mechanism of Action: What We Know
Modafinil does not act as a direct norepinephrine agonist. Instead, it indirectly enhances norepinephrine signaling by influencing upstream regulatory circuits.
Dopamine Transporter Inhibition
Modafinil weakly inhibits the dopamine transporter (DAT), increasing extracellular dopamine. This dopaminergic activity, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, indirectly stimulates norepinephrine neurons.
Effects on Orexin and Histamine Systems
Modafinil activates orexin-producing neurons in the hypothalamus. Orexin, in turn, excites the locus coeruleus, leading to increased norepinephrine release.
Modafinil Interaction with Norepinephrine
This is where the science becomes particularly interesting.
Activation of the Locus Coeruleus
Modafinil increases firing rates in the locus coeruleus. Think of this nucleus as the brain’s alertness amplifier. When it fires, norepinephrine floods cortical and subcortical regions.
Increased Norepinephrine Signaling
Rather than causing a surge, modafinil produces a steady elevation in norepinephrine tone enough to enhance focus without triggering overstimulation.
Cortical Effects
In the prefrontal cortex, increased norepinephrine improves executive functions such as planning, attention regulation, and impulse control.
Subcortical Effects
In subcortical regions, norepinephrine enhances vigilance and sensory responsiveness, reducing mental fatigue.
Cognitive Effects Mediated by Norepinephrine
The cognitive benefits of modafinil are largely norepinephrine-driven.
Attention and Vigilance
Norepinephrine sharpens attentional focus by increasing the signal to noise ratio in neural circuits. This is why users often describe modafinil as “quietly focusing” rather than stimulating.
Executive Function and Working Memory
Optimal norepinephrine levels enhance working memory through alpha-2A adrenergic receptor activation in the prefrontal cortex.
Motivation and Mental Energy
By sustaining cortical arousal, norepinephrine reduces perceived effort, making mentally demanding tasks feel more manageable.
Modafinil vs Traditional Stimulants
On the surface, modafinil looks like a stimulant. Neurochemically, it behaves very differently.
Comparison with Amphetamines
Amphetamines cause massive release of dopamine and norepinephrine. Modafinil increases these neurotransmitters modestly and indirectly, resulting in fewer side effects and lower abuse potential.
Comparison with Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate blocks dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake aggressively. Modafinil’s effects are more selective and physiologically balanced.
Clinical Implications
From a physician’s perspective, these differences matter.
Narcolepsy and Sleep-Wake Disorders
In narcolepsy, impaired orexin signaling leads to unstable wakefulness. Modafinil compensates by enhancing norepinephrine-driven arousal pathways.
ADHD and Off-Label Cognitive Use
Some patients with ADHD benefit from modafinil due to its prefrontal norepinephrine effects, particularly when traditional stimulants are poorly tolerated.
Fatigue in Neurological and Medical Conditions
Multiple sclerosis, depression, and cancer-related fatigue may respond to modafinil through improved norepinephrine-mediated cortical activation.
Side Effects and Safety Considerations
No neuroactive drug is without risk.
Norepinephrine-Related Side Effects
Excessive norepinephrine can cause anxiety, irritability, and insomnia typically dose-dependent.
Cardiovascular Considerations
Because norepinephrine affects vascular tone, monitoring is essential.
Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
Most patients experience minimal changes, but those with pre-existing cardiovascular disease require caution.
Long-Term Neuroadaptation
What happens with prolonged use?
Tolerance and Neuroplasticity
Current evidence suggests minimal tolerance compared to stimulants, likely due to modafinil’s indirect mechanism.
Dependence Potential
Low dopamine spikes and stable norepinephrine modulation translate into a low risk of dependence.
Individual Variability in Response
Not everyone experiences modafinil the same way.
Genetic Factors
Polymorphisms in dopamine and adrenergic receptors influence response intensity.
Baseline Neurotransmitter Tone
Individuals with low baseline norepinephrine may experience more pronounced benefits.
Future Research Directions
The story is not finished.
Unanswered Questions
Precise receptor-level interactions and long-term neuroadaptive changes remain under investigation.
Potential Therapeutic Innovations
Understanding modafinil’s norepinephrine modulation could lead to next-generation cognitive enhancers with improved safety profiles.
Conclusion
From a scientific and clinical standpoint, modafinil represents a refined approach to enhancing wakefulness. By indirectly modulating norepinephrine rather than overwhelming the brain with neurotransmitter surges it supports alertness, focus, and cognitive endurance in a physiologically elegant way. This nuanced interaction explains why modafinil occupies a unique position between medication and cognitive tool.
FAQ
1. Does modafinil directly increase norepinephrine levels?
No. It increases norepinephrine indirectly by activating upstream neural circuits.
2. Why does modafinil feel different from caffeine or amphetamines?
Because it produces stable norepinephrine signaling rather than rapid spikes.
3. Is norepinephrine responsible for modafinil’s focus-enhancing effects?
Largely yes, particularly in the prefrontal cortex.
4. Can modafinil cause anxiety through norepinephrine?
At higher doses, increased norepinephrine may contribute to anxiety.
5. Is modafinil safer than traditional stimulants?
From a neurochemical perspective, its norepinephrine modulation is more controlled and generally better tolerated.
‼️ Disclaimer: The information provided in this article about modafinil is intended for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical consultation or recommendations. The author of the article are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or actions based on the information provided.
References:
- Ballon JS, Feifel D. A systematic review of modafinil: potential clinical uses and mechanisms of action. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006
- McClellan, K. J., & Spencer, C. M. Modafinil: A review of its pharmacology and clinical efficacy in the management of narcolepsy. CNS Drugs, 311–324. https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-199809040-00006 . 1998.
- Willavize, S. A., Nichols, A. I., & Lee, J. Population pharmacokinetic modeling of armodafinil and its major metabolites. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.800 . 2016
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. PROVIGIL. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/020717s037s038lbl.pdf . 2015
- Gilleen, J., Michalopoulou, P. G., Reichenberg, A., Drake, R., Wykes, T., Lewis, S. W., & Kapur, S. Modafinil combined with cognitive training is associated with improved learning in healthy volunteers a randomised controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 529–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2014.01.001 . 2014
- Greenblatt, K., Adams, N. Modafinil. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531476/ . 2025
- Oliva Ramirez A, Keenan A, Kalau O, Worthington E, Cohen L, Singh S. Prevalence and burden of multiple sclerosis-related fatigue: a systematic literature review. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-021-02396-1 . 2021.
- Mereu, M., Bonci, A., Newman, A. H., & Tanda, G. The neurobiology of modafinil as an enhancer of cognitive performance and a potential treatment for substance use disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3232-4 . 2013
- Ciancio A, Moretti MC, Natale A, Rodolico A, Signorelli MS, Petralia A. Personality Traits and Fatigue in Multiple Sclerosis: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134518 . 2023
- Natsch, A. What makes us smell: The biochemistry of body odour and the design of new deodorant ingredients. CHIMIA International Journal for Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.2533/chimia.2015.414 . 2015